Calculated Cache
Calculated cache refers to mapping the current object id to the calculated value of the user-defined complex calculated property.
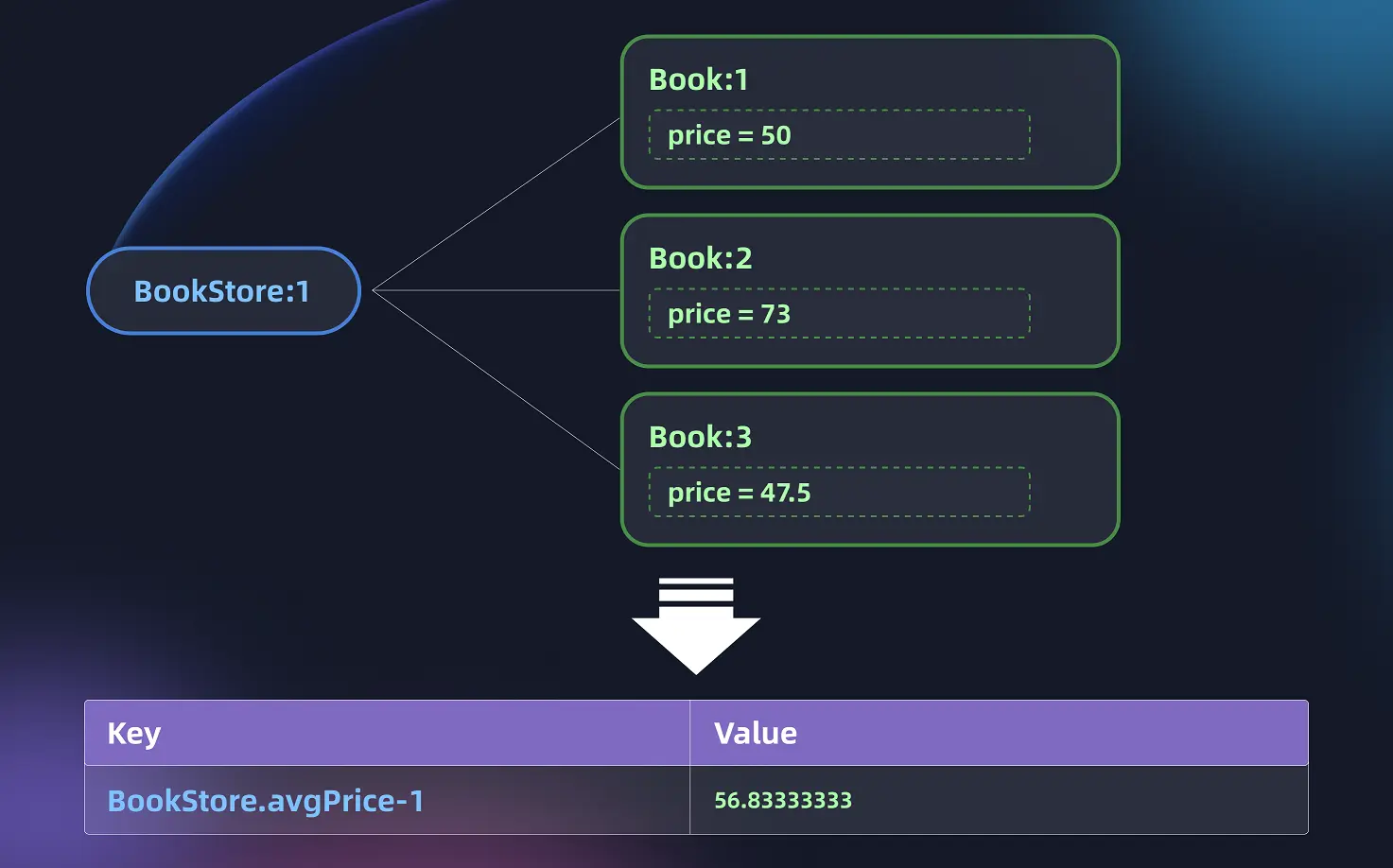
Calculated Property Recap
In the Complex Calculated Properties article, we discussed complex calculated properties in detail.
This article focuses on calculated cache and does not repeat the introduction to complex calculated properties. Please read complex calculated properties before reading this article.
In this article, we will add cache support for the calculated property BookStore.avgPrice defined in complex calculated properties.
To simplify the documentation, this article only discusses BookStore.avgPrice and does not discuss the other association-based calculated property BookStore.newestBooks. Readers can read and run the following official examples:
- jimmer-examples/java/jimmer-sql
- jimmer-examples/java/jimmer-sql-graphql
- jimmer-examples/kotlin/jimmer-sql-kt
- jimmer-examples/kotlin/jimmer-sql-graphql-kt
Enable Calculated Cache
- Java
- Kotlin
@Bean
public CacheFactory cacheFactory(
RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
ObjectMapper objectMapper
) {
return new CacheFactory() {
@Override
public Cache<?, ?> createObjectCache(@NotNull ImmutableType type) {
...omit code...
}
@Override
public Cache<?, ?> createAssociatedIdCache(@NotNull ImmutableProp prop) {
...omit code...
}
@Override
public Cache<?, List<?>> createAssociatedIdListCache(@NotNull ImmutableProp prop) {
...omit code...
}
@Override
public Cache<?, ?> createResolverCache(ImmutableProp prop) {
return createPropCache(
prop,
Duration.ofMinutes(1),
Duration.ofHours(1)
);
}
private <K, V> Cache<K, V> createPropCache(
ImmutableProp prop,
Duration caffeineDuration,
Duration redisDuration
) {
return new ChainCacheBuilder<>()
.add(
CaffeineValueBinder
.forProp(prop)
.maximumSize(512)
.duration(caffeineDuration)
.build()
)
.add(
RedisValueBinder
.forProp(prop)
.redis(connectionFactory)
.objectMapper(objectMapper)
.duration(redisDuration)
.build()
)
.build();
}
};
}
@Bean
fun cacheFactory(
connectionFactory: RedisConnectionFactory,
objectMapper: ObjectMapper
): KCacheFactory {
return object: KCacheFactory {
override fun createObjectCache(type: ImmutableType): Cache<*, *>? =
...omit code...
override fun createAssociatedIdCache(prop: ImmutableProp): Cache<*, *>? =
...omit code...
override fun createAssociatedIdListCache(prop: ImmutableProp): Cache<*, List<*>>? =
...omit code...
override fun createResolverCache(prop: ImmutableProp): Cache<*, *> =
return createPropCache(
prop,
Duration.ofMinutes(1),
Duration.ofHours(1)
)
private fun <K, V> createPropCache(
prop: ImmutableProp, duration: Duration): Cache<K, V> =
ChainCacheBuilder<Any, Any>()
.add(
CaffeineValueBinder
.forProp(prop)
.maximumSize(512)
.duration(caffeineDuration)
.build()
)
.add(
RedisValueBinder
.forProp(prop)
.redis(connectionFactory)
.objectMapper(objectMapper)
.duration(redisDuration)
.build()
)
.build()
}
}
Usage
- Java
- Kotlin
BookStoreTable table = Tables.BOOK_STORE_TABLE;
List<BookStore> stores = sqlClient
.createQuery(table)
.select(
table.fetch(
Fetchers.BOOK_STORE_FETCHER
.allScalarFields()
.avgPrice()
)
)
.execute();
System.out.println(stores);
val stores = sqlClient
.createQuery(BookStore::class) {
select(
table.fetchBy {
allScalarFields()
avgPrice()
}
)
}
.execute()
println(stores)
-
Step 1: Query aggregate root
First, query the aggregate root object, executing the following SQL:
select
tb_1_.ID,
tb_1_.NAME,
tb_1_.WEBSITE
from BOOK_STORE tb_1_The query in the code is implemented here to obtain some BookStore objects. Such objects obtained by direct user queries are called aggregate root objects.
cautionJimmer does not cache aggregate objects returned by user queries, because the consistency of such query results cannot be guaranteed.
Even if cache them at the cost of sacrificing consistency is required, it is a business need of the user rather than the framework.
-
Step 2: Convert current object id to calculated value via calculated cache
The above code will return a series of aggregate root objects. If using the official sample data in the database, it will return two aggregate root objects.
The object fetcher in the code contains the calculated property
BookStore.avgPriceThe primary keys
IDof these 2 BOOK_STOREs are 1 and 2.Jimmer first looks up the data in Redis with keys
BookStore.avgPrice-1andBookStore.avgPrice-2.Suppose the data corresponding to these keys cannot be found in Redis:
127.0.0.1:6379> keys BookStore.avgPrice-*
(empty array)So the following SQL is executed to compute the calculated property:
select
tb_1_.ID,
avg(tb_2_.PRICE)
from BOOK_STORE tb_1_
left join BOOK tb_2_
on tb_1_.ID = tb_2_.STORE_ID
where
tb_1_.ID in (
? /* 1 */, ? /* 2 */
)
group by
tb_1_.IDJimmer will put the query results into Redis, so we can view this data in Redis:
127.0.0.1:6379> keys BookStore.avgPrice-*
1) "BookStore.avgPrice-2"
2) "BookStore.avgPrice-1"
127.0.0.1:6379> get BookStore.avgPrice-1
"58.5"
127.0.0.1:6379> get BookStore.avgPrice-2
"80.333333"
127.0.0.1:6379>Thus, the two
BookStoreobjects can obtain the average price of their respective books through their calculated propertyBookStore.avgPrice.Undoubtedly, before the data in Redis expires, executing the Java/Kotlin code above again will directly return the calculated data from Redis without generating the second SQL statement.
Finally, Jimmer concatenates the results of the 3 steps as the final data returned to the user:
[
{
"id":2,
"name":"MANNING",
"website":null,
"avgPrice":58.5
},
{
"id":1,
"name":"O'REILLY",
"website":null,
"avgPrice":80.333333
}
]
Cache Invalidation
Responding to Triggers
Unlike the fully automatic cache invalidation of object cache and association cache, maintaining the consistency of calculated cache requires user assistance.
This is because calculated properties introduce custom calculation rules that the ORM framework cannot understand.
For the calculated property BookStore.avgPrice, the following two cases will both invalidate the calculated cache:
-
Modifying the
STORE_IDforeign key field of theBOOKrecord will affect theavgPricecache data of the two bookstores corresponding to the old and new values. -
Modifying the
PRICEfield of theBOOKrecord will invalidate theavgPricecache data of the bookstore it belongs to.
In the Complex Calculated Properties article, a class BookStoreAvgPriceResolver is defined to support the calculated property BookStore.avgPrice. The code is as follows:
- Java
- Kotlin
package com.example.business.resolver;
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.*;
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.TransientResolver;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BookStoreAvgPriceResolver implements TransientResolver<Long, BigDecimal> {
@Override
public Map<Long, BigDecimal> resolve(Collection<Long> ids) {
...omit code...
}
@Override
public BigDecimal getDefaultValue() {
...omit code...
}
}
package com.example.business.resolver
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.*
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.kt.KTransientResolver
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component
@Component
class BookStoreAvgPriceResolver(
...omit...
) : KTransientResolver<Long, BigDecimal> {
override fun resolve(ids: Collection<Long>): Map<Long, BigDecimal> {
...omit code...
}
override fun getDefaultValue(): BigDecimal =
...omit code...
}
We need to override the following two methods in this class:
- Java
- Kotlin
package com.example.business.resolver;
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.*;
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.TransientResolver;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BookStoreAvgPriceResolver implements TransientResolver<Long, BigDecimal> {
// Constructor inject sqlClient
private final JSqlClient sqlClient;
...other code omitted...
@Override
Collection<?> getAffectedSourceIds(@NotNull EntityEvent<?> e) {
// TODO
}
@Override
Collection<?> getAffectedSourceIds(@NotNull AssociationEvent e) {
// TODO
}
}
package com.example.business.resolver
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.*
import org.babyfish.jimmer.sql.kt.KTransientResolver
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component
@Component
class BookStoreAvgPriceResolver(
// Constructor inject sqlClient
private val sqlClient: KSqlClient
) : KTransientResolver<Long, BigDecimal> {
...other code omitted...
override fun getAffectedSourceIds(e: EntityEvent<*>): Collection<*>? {
// TODO
}
override fun getAffectedSourceIds(e: AssociationEvent): Collection<*>? {
// TODO
}
}
These two methods are the built-in trigger response methods of TransientResolver that are executed automatically when the database changes. They are responsible for automatically clearing the computed cache when the database changes.
Next, let's implement these two methods.
When BOOK.STORE_ID is modified
Users can change the association between BOOK_STORE and BOOK by modifying the STORE_ID foreign key of the BOOK table. This will inevitably affect BookStore.avgPrice of some bookstores.
If watching for changes to the Book.store one-to-many association, the old and new values before and after the modification are two parent objects that need to be considered separately, making the code slightly more cumbersome.
Luckily, the entity model in this example has the reverse one-to-many association BookStore.books. When listening for changes to BookStore.books, we only need to consider the id of the current BookStore object, simplifying the code.
Implement getAffectedSourceIds(AssociationEvent) as follows:
- Java
- Kotlin
@Override
public Collection<?> getAffectedSourceIds(AssociationEvent e) {
if (sqlClient.getCaches().isAffectedBy(e) && ❶
e.getImmutableProp() == BookStoreProps.BOOKS.unwrap() ❷
) {
return Collections.singletonList(e.getSourceId()); ❸
}
return null;
}
override fun getAffectedSourceIds(e: AssociationEvent): Collection<*>? {
if (sqlClient.caches.isAffectedBy(e) && ❶
e.immutableProp == BookProps.BOOKS ❷
) {
return listOf(e.sourceId) ❸
}
return null
}
-
❶ If the trigger type is set to
BOTH, any modification-caused trigger event notifications will be executed twice.noteThe 1st time:
e.connectionis non-null, indicating this is a notification from the Transaction trigger.The 2nd time:
e.connectionis null, indicating this is a notification from the BinLog trigger.However, the cache consistency maintenance work only needs to be done once, no need to do it twice.
sqlClient.caches.isAffectedBy(e)can solve this problem, so that even if the trigger type is set toBOTH, the code here will only execute once.cautionNo matter whether Jimmer's trigger type is set to
BOTHor not, it is recommended to include this check as a disciplinary measure. -
❷ If the
BookStore.booksone-to-many association is modified -
❹ Then the
sourceIdof this association modification event (i.e. theBookStoreid) needs to have the computed property cacheBookStore.avgPricecleared.
Now let's verify the effect of modifying Book.store:
-
If BinLog trigger is enabled, modifying the database by any means can lead to Jimmer's cache consistency intervention. For example, directly execute the following SQL in the SQL IDE:
update BOOK
/* Old value: 1, New value: 2 */
set STORE_ID = 2
where ID = 7; -
If only Transaction trigger is enabled, Jimmer's API must be used to modify the database:
- Java
- Kotlin
BookTable table = Tables.BOOK_TABLE;
sqlClient
.createUpdate(table)
// Old value: 1L, New value: 2L
.set(table.store().id, 2L)
.where(table.id().eq(7L))
.execute();sqlClient
.createUpdate(Book::class) {
// Old value: 1L, New value: 2L
set(table.store.id, 2L)
where(table.id eq 7L)
}
.execute()
Regardless of which way above is used to modify the data, you will see the following log output:
Delete data from redis: [Book-7]
Delete data from redis: [Book.store-7]
Delete data from redis: [BookStore.avgPrice-1] ❶
Delete data from redis: [BookStore.books-1]
Delete data from redis: [BookStore.avgPrice-2] ❷
Delete data from redis: [BookStore.books-2]
-
❶ The calculated cache
BookStore.avgPrice-1of the parent object referenced by the old foreign key1is deleted. -
❷ The calculated cache
BookStore.avgPrice-2of the parent object referenced by the new foreign key2is deleted.
Modifying BOOK.PRICE
Users can also modify the price of books, which will inevitably affect BookStore.avgPrice of the bookstore it belongs to.
Implement getAffectedSourceIds(EntityEvent<?>):
- Java
- Kotlin
@Override
public Collection<?> getAffectedSourceIds(EntityEvent<?> e) {
if (sqlClient().getCaches().isAffectedBy(e) && ❶
!e.isEvict() && ❷
e.getImmutableType().getJavaClass() == Book.class) { ❸
Ref<BookStore> storeRef = e.getUnchangedRef(BookProps.STORE); ❹
if (storeRef != null && storeRef.getValue() != null && e.isChanged(BookProps.PRICE)) { ❺
return Collections.singletonList(storeRef.getValue().id()); ❻
}
}
return null;
}
override fun getAffectedSourceIds(e: EntityEvent<*>): Collection<*>? {
if (sqlClient.caches.isAffectedBy(e) && ❶
!e.isEvict && ❷
e.getImmutableType().javaClass == Book::class.java ❸
) {
val store = e.getUnchangedRef(Book::store)?.value ❹
if (store !== null && e.isChanged(Book::price)) { ❺
return listOf(store.id) ❻
}
}
return null
}
-
❶ If the trigger type is set to
BOTH, any modification-caused trigger event notifications will be executed twice.noteThe 1st time:
e.connectionis non-null, indicating this is a notification from the Transaction trigger.The 2nd time:
e.connectionis null, indicating this is a notification from the BinLog trigger.However, the cache consistency maintenance work only needs to be done once, no need to do it twice.
sqlClient.caches.isAffectedBy(e)can solve this problem, so that even if the trigger type is set toBOTH, the code here will only execute once.cautionNo matter whether Jimmer's trigger type is set to
BOTHor not, it is recommended to include this check as a disciplinary measure. -
❷ There are two reasons for Jimmer's event callbacks, whether it's
EntityEventorAssociationEvent.-
Explicitly know that the database has been modified
In this case,
isEvict()returns false. Users can access any property ofEntityEvent/AssociationEvent. -
In the process of automatic cache eviction with cascading effect, the cache of an object/association needs to be evicted
In this case,
isEvict()returns true. Except forEntityEvent.id/AssociationEvent.sourceId, the event object does not support any other properties likeEntityEvent.newEntity,AssociationEvent.attachedTargetId.Here, we need to explicitly determine if the user has modified the
PRICEfield of theBOOKtable, so we must checkisEvict()is false.warningWhether to check
e.isEvict()must be decided on a case-by-case basis.
-
-
❸ Confirm that the current event was triggered because an object of type
Bookwas modified. -
❹ ❺
e.getUnchangedRef(BookProps.STORE)/e.getUnchangedRef(Book::store)returns aRefwrapper object containing the unchanged associated object (only id property) or null, if theBook.storeassociation based on foreign key was not modified.info-
If the returned
Refwrapper object itself is null, it means this property was modified rather than beingUnchanged. -
If the returned
Refwrapper object is non-null but its internalvalueis null, it means this property was not modified and its value has remained null all along.
Ultimately, we expect the
BOOK.STORE_IDforeign key field was not modified and has remained non-null.tipWe don't need to consider the case where the foreign key field was modified here, because the other method we discussed earlier,
getAffectedSourceIds(AssociationEvent), will properly handle that case. -
-
❻ If all the above conditions are met, then the computed property cache
BookStore.avgPriceof theBookStoreparent object that theprice-modifiedBookbelongs to needs to be cleared.
Now let's verify the effect of modifying Book.price:
- If BinLog trigger is enabled, modifying the database by any means can lead to Jimmer's cache consistency intervention. For example, directly execute the following SQL in the SQL IDE:
update BOOK
set PRICE = PRICE + 1
where ID = 7;
-
If only Transaction trigger is enabled, Jimmer's API must be used to modify the database:
- Java
- Kotlin
BookTable table = Tables.BOOK_TABLE;
sqlClient
.createUpdate(table)
.set(table.price(), table.price().plus(BigDecimal.ONE))
.where(table.id().eq(7L))
.execute();sqlClient
.createUpdate(Book::class) {
set(table.price, table.price + BigDecimal.ONE)
where(table.id eq 7L)
}
.execute()
Regardless of which way above is used to modify the data, you will see the following log output:
Delete data from redis: [BookStore.avgPrice-1] ❶
Delete data from redis: [Book-7]
- ❶ The calculated cache
BookStore.avgPrice-1of the parent object referenced by the foreign key is deleted.